 Part Machining / Mould
Part Machining / Mould Sheet Metal / Hand Plate
Customize&Volume Production
 English
English
 Part Machining / Mould
Part Machining / Mould  English
English

Introduction to 3D printing
3D printing overview
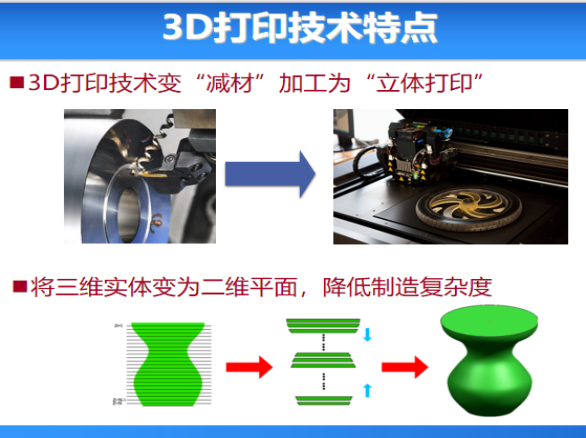
3D printing is a type of rapid prototyping technology. It is a technology that uses adhesive materials such as powdered metal or plastic to construct objects by stacking them layer by layer based on digital model files (i.e. "Laminated modeling method")
In the past, it was often used to make models in the fields of mold manufacturing, industrial design and other fields. Now it is gradually used in the direct manufacturing of some products. In particular, some high-value applications (such as joints or teeth, or some aircraft parts) already have parts printed using this technology, which means the popularity of "3D printing" technology.
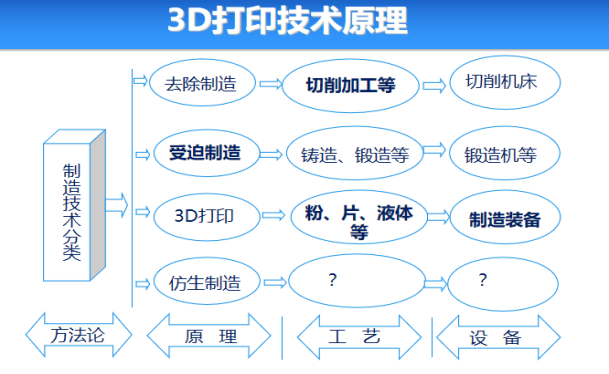
3D printing technology principles
3D printing technology (called additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping, etc. in academia) is to obtain accumulation constraints, paths and methods through discrete analysis of CAD data, and form a three-dimensional solid model through the superposition and accumulation of materials. Based on the principles of discreteness and accumulation, it is also It's called "lamination manufacturing." To learn 3D printing technology, you need to have basic computer operation knowledge, three-dimensional design software, mechanical basics, control basics, network information and other multi-disciplinary knowledge.
Application areas
At present, 3D printing technology has been widely used in aerospace, national defense, automobile manufacturing, industrial molds, medical rehabilitation, education and scientific research and other fields. 3D printing technology is used in major national aerospace projects such as China's Tianwen-1 probe and Zhurong Mars rover, China Space Station, China's manned space project, domestic large aircraft C919, and Yun-20. In addition, 3D printing technology has mature applications in daily life such as automobile parts manufacturing, conformal waterways/thermoplastic molds, orthopedic implants, etc.

3D printing process
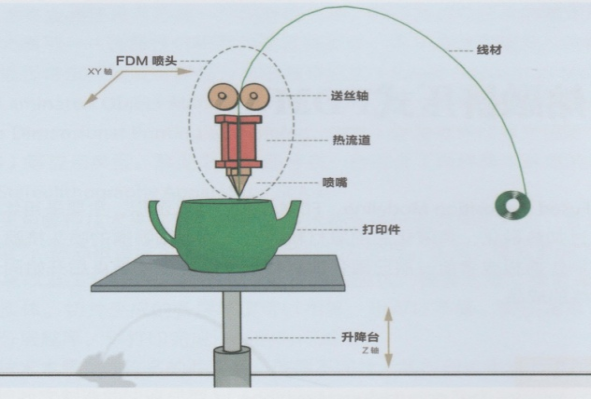
3D printing process:FDM
Fused Deposition Manufacturing (FDM) mainly uses filamentary hot-melt materials as raw materials, which are melted by heating, and then extruded through a fine nozzle. According to the layered cross-sectional information of the part, according to a certain path, Coating is carried out layer by layer on the forming plate or workbench. When the temperature is lower than the melting point, solidification and deposition begin, and then the final product is formed layer by layer.
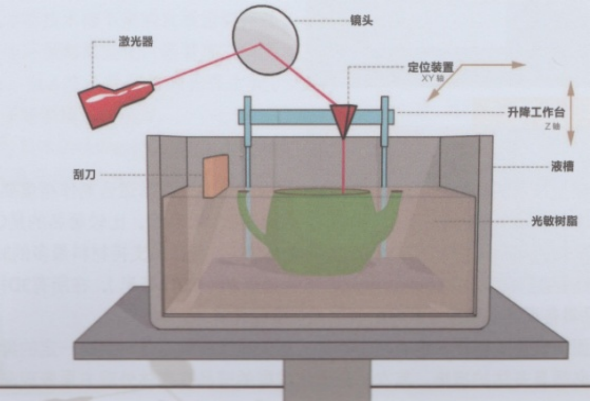
3D printing process: SLA
Stereo Lithography Appearance uses photosensitive resin as raw material and is solidified and formed layer by layer through a computer-controlled ultraviolet laser emitting device.
3D printing process: LOM
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) mainly uses foil materials (such as paper, metal foil, plastic film) with hot melt adhesive on the back as raw materials, which are cut layer by layer by a laser and then bonded together in sequence.
3D printing process: SLS
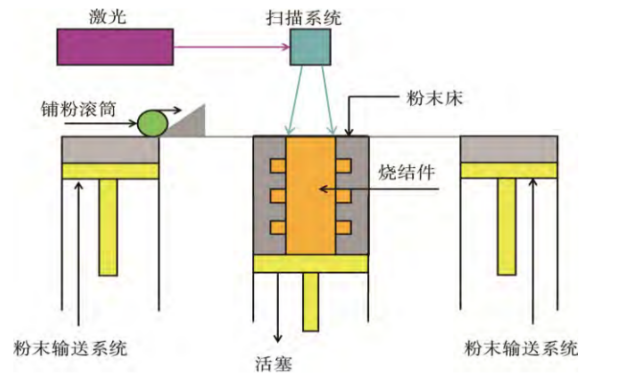
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses the basic principle of high-temperature sintering of powder materials under laser irradiation. During the forming process, the laser partially melts the powder materials, and the powder particles retain their solid phase form and pass through the subsequent liquid phase solidification. The solid particles are rearranged and bonded to achieve powder densification.
3D printing process: SLM
The technical process of selective laser melting (SLM) is basically the same as that of SLS. Most of the materials used are mixtures of different metals, and each component compensates for each other during the sintering process.
3D printing process: 3-DP
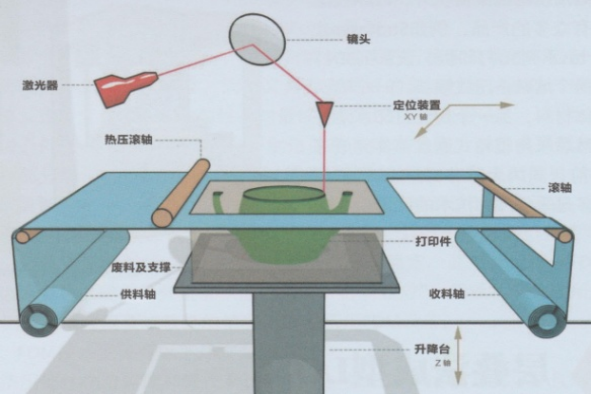
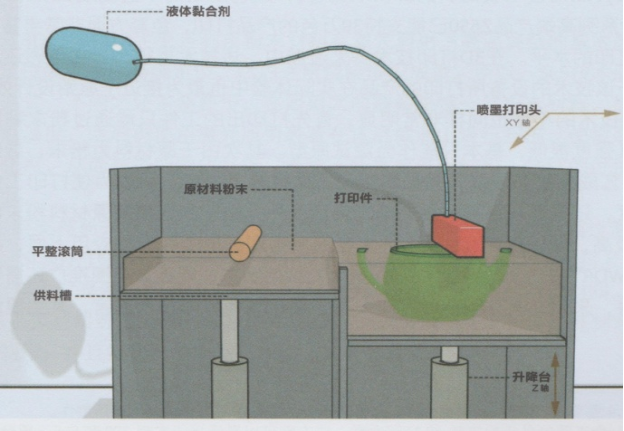
Three-Dimensional Printing uses powder materials and uses a nozzle to spray adhesive on the area that needs to be formed, allowing the material powder to bond to form a local cross-section, and the layers are stacked and bonded to form.
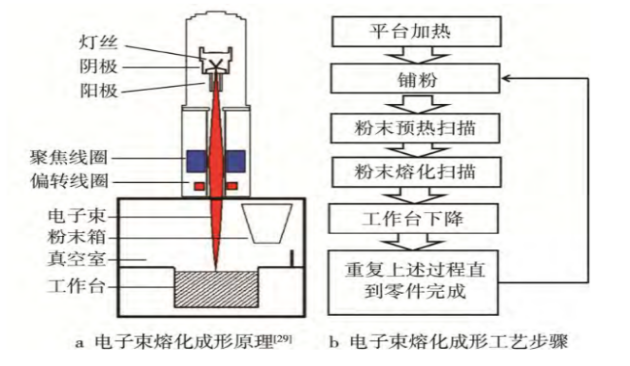
3D printing process: EBM
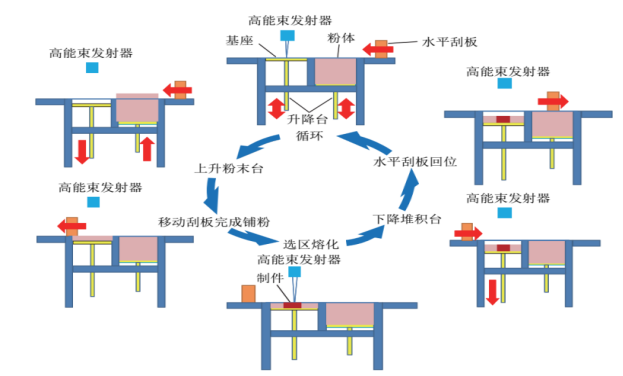
Electron Beam Melting (EBM) uses high-energy and high-speed electron beams to selectively melt metal powder layers or metal wires in a vacuum environment, melt and shape them, and stack them layer by layer until the entire solid metal part is formed.
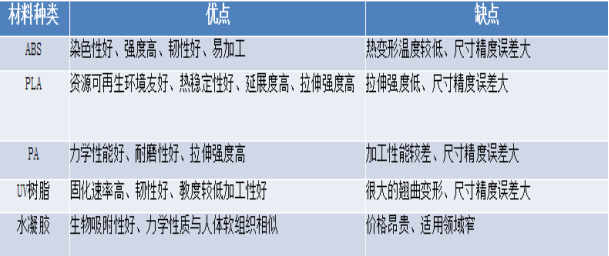
3D printing materials
The material requirements of the 3D printing process: It is conducive to the rapid and accurate processing of prototype parts, and it is conducive to the subsequent processing process to try to meet the product requirements for strength, stiffness, moisture resistance, thermal stability, etc. 3D printing materials can be divided into three categories: polymer materials, metal materials and inorganic non-metallic materials. They can be divided into two categories according to their form: liquid materials and solid materials (filaments, flakes, powders, etc.)
Corporate Style: Shenzhen Industrial People
Shenzhen Industrial Rapid Prototyping Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2004. The company has a professional engineering team of 300+ people and an engineering team of 40 people to fully meet the needs of every customer. The company has professional production equipment, such as 200 3D printing, CNC, turning and milling machines, five-axis CNC, stamping equipment, vacuum molding machines, injection molding machines, etc., totaling more than 500 units. Industrial people strictly control quality. The inspection process is equipped with precision detection and uses Zeiss measuring instruments. The quality inspection process is controlled by Japanese technology. We support customization with drawings and samples, and provide customers with very competitive solutions and free sample production for product mass production!
